■ Cloud-based Vehicular Networks
In the era of the Internet of Things, all components in intelligent transportation systems will be connected to improve transport safety, relieve traffic congestion, reduce air pollution, and enhance the comfort of driving. The vision of all vehicles connected poses a significant challenge to the collection and storage of large amounts of traffic-related data. In our work, we propose to integrate cloud computing into vehicular networks such that the vehicles can share computation resources, storage resources, and bandwidth resources. The proposed architecture includes a vehicular cloud, a roadside cloud, and a central cloud. Then we study cloud resource allocation and virtual machine migration for effective resource management in this cloud-based vehicular network. A game-theoretical approach is presented to optimally allocate cloud resources. Virtual machine migration due to vehicle mobility is solved based on a resource reservation scheme.
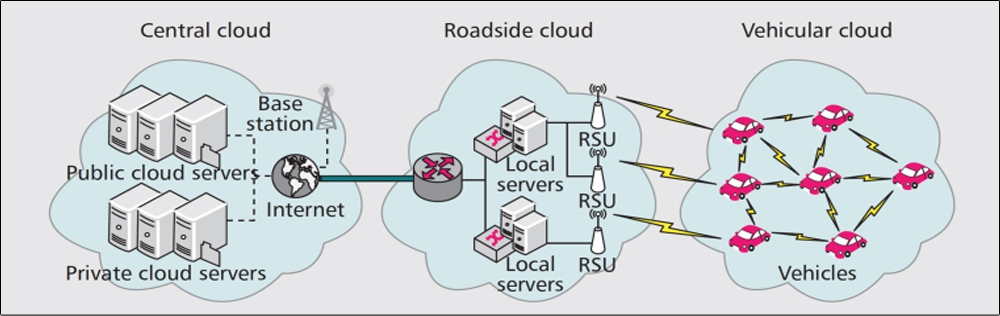
Fig. 1 Proposed cloud-based vehicular network architecture.
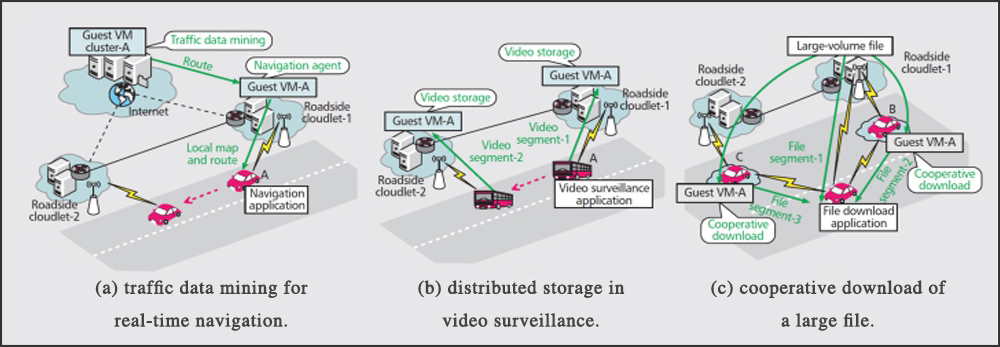
Fig. 2 Applications of cloud-based vehicular network.
■ Cooperative Resource Management in Vehicular Networks
In cloud-based vehicular networks, there exist multiple cloud service providers (CSPs), who build up the cloud infrastructures and provide cloud services for the vehicles of the Intelligent Transportation System (ITS). In such vehicular networks, both the bandwidth and computing resources should be efficiently exploited to improve the quality of services (QoS) of vehicular applications. We propose that CSPs can cooperate to form coalitions to share their idle resources with each other. We set up a coalition game model based on two-sided matching theory for cooperation among CSPs to share their idle resources. As a result, the resources can be better utilized, and the QoS for users can be improved. Numerical results indicate that our scheme can improve resource utilization and increase by 75% the QoS of the applications compared with that without cooperation. Moreover, the higher service cost of cooperation brings negative effect on coalition formation. The higher cooperation willingness of CSPs and the lower service cost support more service applications.
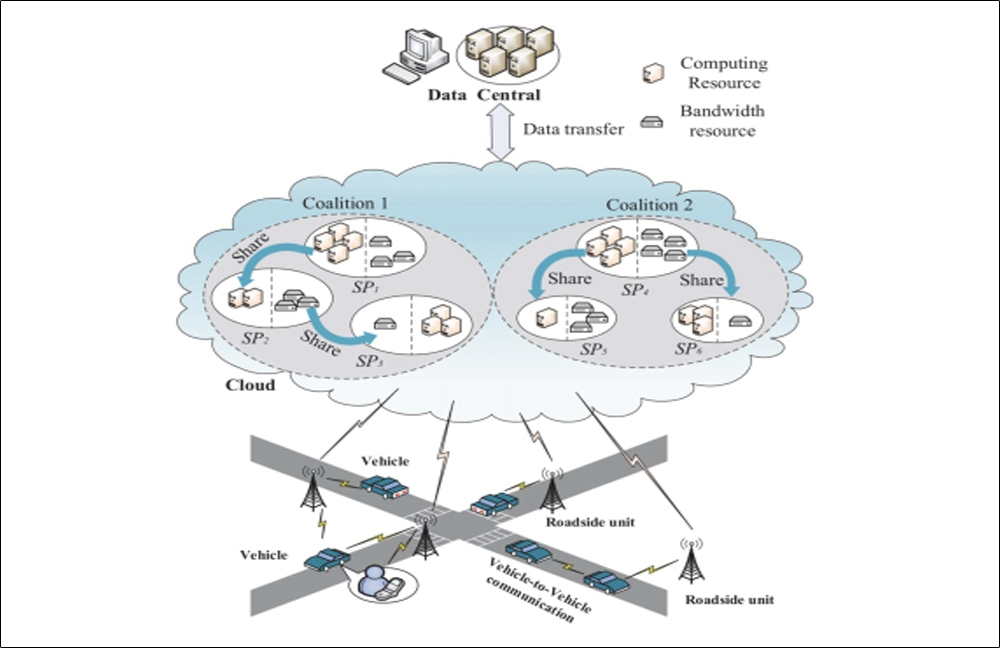
Fig. 3 Resource coalition in vehicular networks.
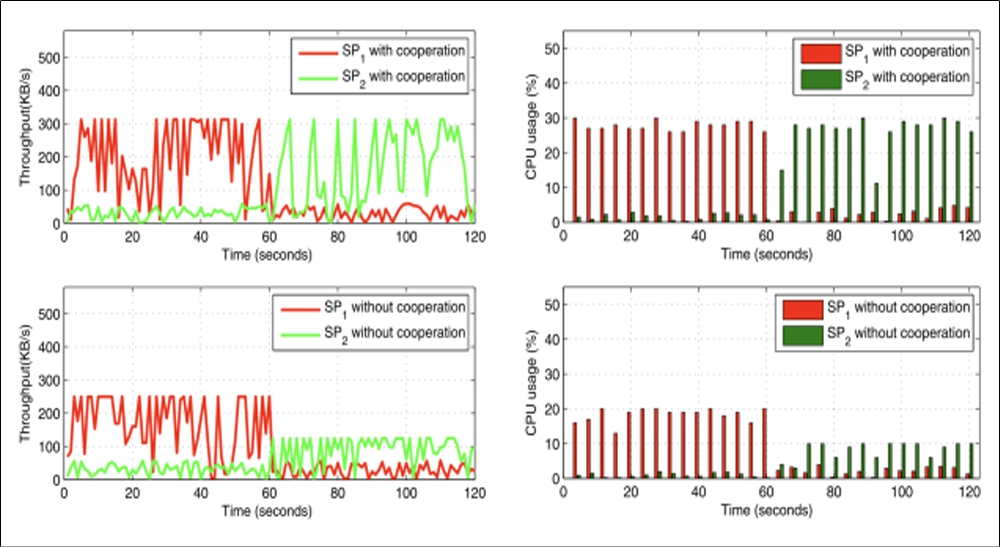
Fig. 4 Performance Evalution.
■ Security and Privacy Protection in Vehicular Networks
Traditional Vehicular Ad hoc Networks (VANETs) is evolving towards Vehicular Social Networks (VSNs), which reflects some essential features due to people’s social activities. The security and privacy protection in VSNs is a challenging problem. Take the location privacy for example. In traditional pseudonym-based solutions, the privacy-preserving strength is mainly dependent on the number of vehicles meeting at the same occasion. We notice that an individual vehicle actually has many chances to meet several other vehicles. In most meeting occasions, there are only few vehicles appearing concurrently. Motivated by these observations, we propose a new privacy-preserving scheme, called MixGroup, which is capable of efficiently exploiting the sparse meeting opportunities for pseudonym changing. By integrating the group signature mechanism, MixGroup constructs extended pseudonym-changing regions, in which vehicles are allowed to successively exchange their pseudonyms. As a consequence, for the tracking adversary, the uncertainty of pseudonym mixture is accumulatively enlarged, and therefore location privacy preservation is considerably improved. We carry out simulations to verify the performance of MixGroup. Results indicate that MixGroup significantly outperforms the existing schemes. In addition, MixGroup is able to achieve favorable performance even in low traffic conditions.
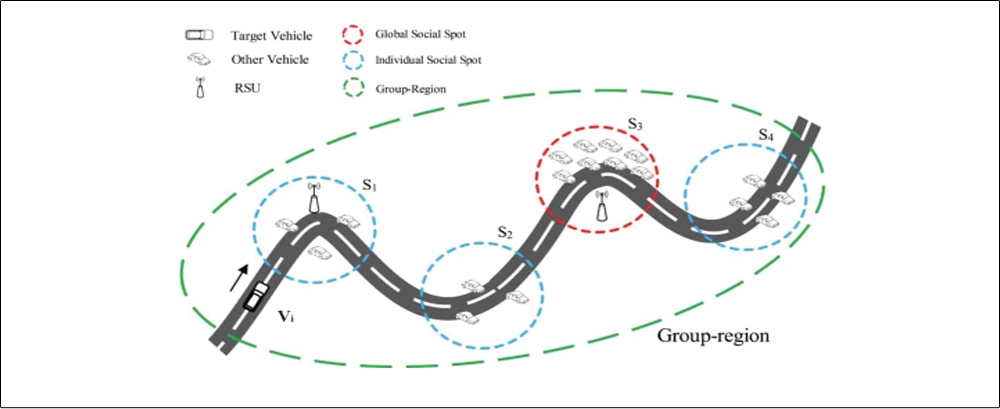
Fig. 5 Illustration of the proposed MixGroup scheme.
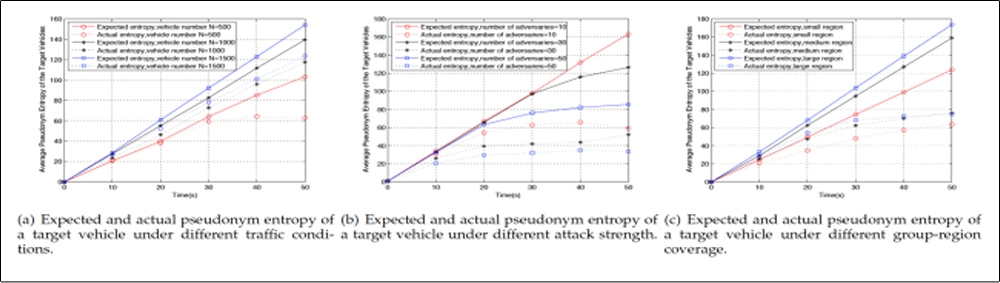
Fig. 6 Expected and Actual pseudonym entropy of a target vehicle.
■ iBus: Vehicular Cloudlet and App for Bus Information Services
Bus network is one of the major components of Intelligent Transport Systems. It is reported that, people statistically spend near half an hour on the road when they take buses. A satisfying bus information service is eagerly needed for many people in improving their experience in buses. We are motivated to develop the iBus system, which consists of a dedicated vehicular cloudlet (hardware subsystem) and a user-end bus App (software subsystem). The vehicular cloudlet is deployed in bus and connected to the bus IC reader. The bus App is designed for user’s mobile phone and bound to the bus IC account. The vehicular cloudlet has a 4G backhaul and provides Wi-Fi coverage in bus. With the iBus system, people in bus will enjoy the Traffic information services, Internet services, multimedia services, commercial services, entertainments, etc., all for FREE!
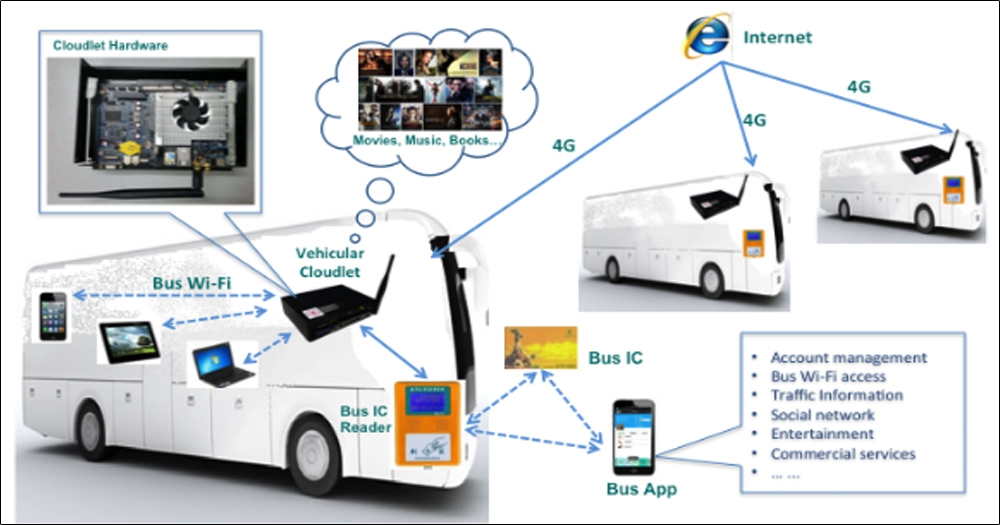
Fig. 7 iBus System.






